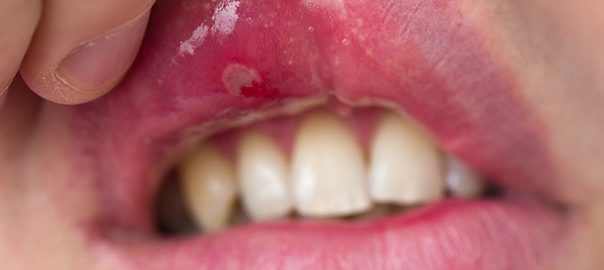
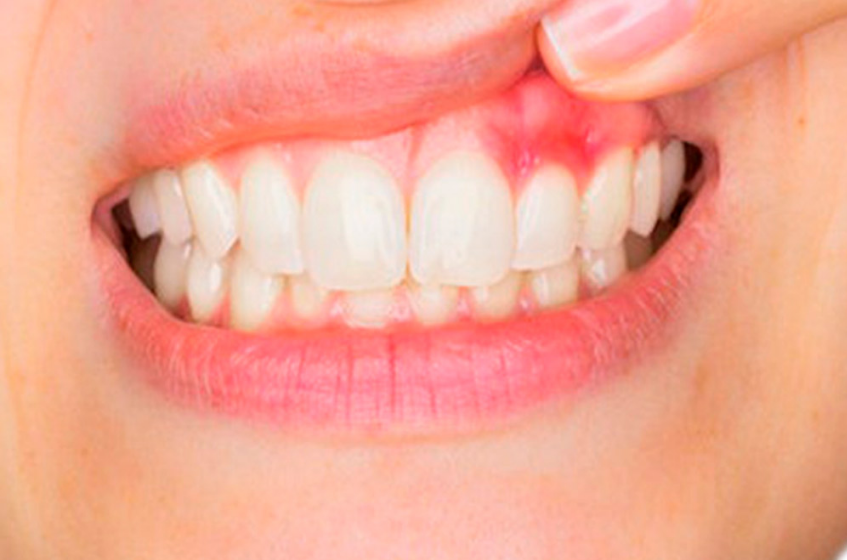
There is emerging evidence suggesting a potential connection between gum disease (periodontitis) and COVID-19 complications. While more research is needed to establish a definitive link, several studies have observed an association between periodontitis and an increased risk of developing severe COVID-19 symptoms. Here’s what we know so far:
- Inflammation and Immune Response: Gum disease is characterized by chronic inflammation and bacterial infection in the gums. This inflammatory response can lead to a dysregulated immune system. COVID-19 is also associated with an excessive immune response, leading to a cytokine storm, which can contribute to severe respiratory complications. It is possible that the preexisting inflammation from gum disease may exacerbate the immune response to COVID-19.
- Shared Risk Factors: Gum disease and COVID-19 share common risk factors, such as older age, diabetes, smoking, and other systemic diseases. These factors may contribute independently to both conditions, making it difficult to determine a direct causal relationship between gum disease and COVID-19 complications.
- Oral Cavity as a Reservoir: The oral cavity serves as a reservoir for various pathogens, including respiratory viruses like SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. It is hypothesized that periodontal pathogens may serve as a source of infection or contribute to the systemic spread of the virus, potentially increasing the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes.
- Limited Clinical Studies: While some observational studies have shown a correlation between gum disease and COVID-19 severity, the evidence is still limited. More rigorous research, including well-controlled clinical trials and larger population studies, is required to establish a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the two.
Given the potential connection and the established importance of oral health for overall well-being, it is advisable to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Individuals with preexisting gum disease should consider seeking appropriate treatment and managing their oral health to reduce the potential risk of complications, including those related to COVID-19. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals, including dentists and physicians, is recommended for personalized advice and guidance.
A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology came up with an interesting fact that there is a strong association between periodontitis and the complications of COVID-19. After examining more than 500 COVID-19 patients the researchers could deduce that those who had gum disease were at a greater risk of getting admitted into ICU, or put on a ventilator support and even more likely to die.